Managing databases / Database replication
Introduction to database replication and its benefits
Introduction
For many modern day applications, their backend is configured using a distributed database. Data is stored and processed using an arrangement, or cluster of database servers, instead of relying on a single database server. The distributed model can ensure that data is still accessible even if one of the database servers suffers a failure. However, the distributed approach introduces the issue of making sure that all of the actors in the distributed system are up to date with the information that the end user is expecting to have returned to them. This introduces us to the topic of this guide: database replication.
In this guide, we will cover what database replication is and discuss the main benefits of having a database replication process in place for your distributed system.
What is database replication?
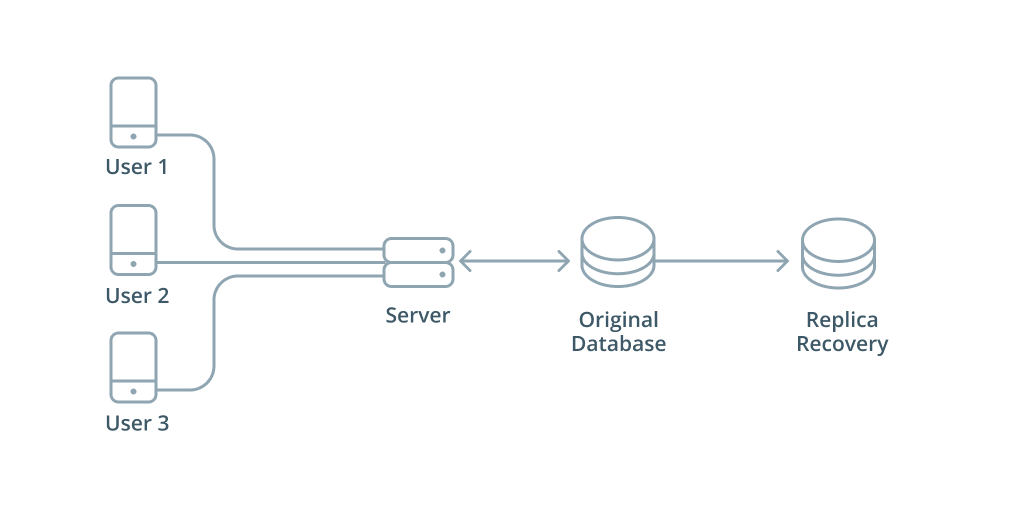
Database replication is the process of maintaining a copy of data on multiple machines that are connected via a network. The process can be visualized like the following, where a lead database is sending its information to followers to replicate:
This image displays a specific kind of database replication architecture, but replication can also be done in different ways. The main goal is always the same, and that goal is to keep multiple, identical copies of up to date data in different places.
Benefits of database replication
As briefly alluded to in the introduction, there are several reasons why one would want to have a distributed database and therefore implement database replication. Some of the most common benefits include the following:
- improve the availability of data
- increase the speed of data access
- enhance server performance
- accomplish preparation for disaster recovery
- improve analytics
Improve the availability of data
Replication improves the availability of data because it prevents relying on a single point of failure and losing database access. If there were some sort of technical glitch, power outage, or any number of different occurrences that affected that single point, then your application would not be able to access the data needed for its proper function.
Data replication enhances the resiliency and reliability of systems by storing data across multiple nodes. If one node goes down, there is another one to step up with the exact same data on it to keep operations running smoothly.
Increase the speed of data access
For organizations both large and small, there may be users located globally. Geographically distributed database replication helps ensure that for any given user in the organization that needs particular data that they can get it in a timely manner and without too much delay.
Replicating data to local servers in the locations near to where it is being accessed provides users with faster data access and queries. If a organization had a single node in the USA, then a user trying to pull data in Europe could experience latency when trying to access it. A organization with a cluster in the USA as well as a replicated cluster in Europe would ensure that this user can work efficiently with the data that they need when they need it.
Enhance server performance
Database replication also reduces the load on the primary server of the database. If data was only able to be accessed on a single server, that server would be handling every request coming to the database. With replication, that load can be dispersed among other nodes in the distributed system. Because all of the nodes have identical replicas of the data, some queries could get handled by secondary nodes and leave the primary to handle only certain reads or only writes.
Saving the primary for handling write operations can prove to be beneficial because if it were handling all reads and writes that may put unwanted strain on the server's resources. Reading from the primary may make sense for a situation where there are not many operations coming in to the database. However, in times of scaling and growth, it is best practice to delegate tasks across a distributed system rather than putting all the load on a single node's plate.
Accomplish preparation for disaster recovery
In the case of a catastrophe, replication also secures recovery of what gets lost or corrupted. While replicas are not backups themselves because they continuously apply changes, they can be a target for your database backups.
For instance, if you want to back up your data, you can turn replication off briefly on one of the secondaries to get data in a consistent state, back up the data when there are no more write operations incoming, and then restart replication to catch back up on new updates. The replica gives you a snapshot of consistent data to target for disaster recovery without interrupting operations.
An additional way replication facilitates preparation for disaster recovery is by explicitly configuring a replica to be a lagging follower. This replica would apply operations with a delay of a defined time. This delay allows the database monitoring team to notice an issue and avoid applying changes to the replica from a corrupted primary. They then can turn off the replication and have a mostly up-to-date server ready and running to keep operations going.
These methods add a level of enhanced data protection that would not be present without database replication.
Improve analytics
Similar to the benefits mentioned from enhancing server performance, replication allows for the dedication of nodes specifically for analytics. By having exact replicas of data available outside of a single site/node, there is now the option to have a secondary that is specifically used only for running analytics on the data.
This makes it so any nodes handling write operations or other heavy reads are not strained also by handling analytics queries from database users. For example, your analytics team that is pulling data to put together user growth reports for the past quarter will have a dedicated node to work with and not strain any of the core nodes. This improves the performance experienced by the analytics team as well as keeping unnecesary load off the primary — all with data that is completely the same and up to date.
Wrapping up
Database replication is an important process to implement for a successful distributed data system. In this article we briefly introduced what database replication is and the benefits it adds to your new or already existing application.
Database replication is not a one size fits all process, so it is important to know what benefits are most important to your team when configuring. We'll take the learned benefits and discuss the most common database replication architectures, methods, and types in additional guides.
To perform database migrations with Prisma Client, use the Prisma Migrate tool. Prisma Migrate analyzes your schema files, generates migration files, and applies them to target databases.